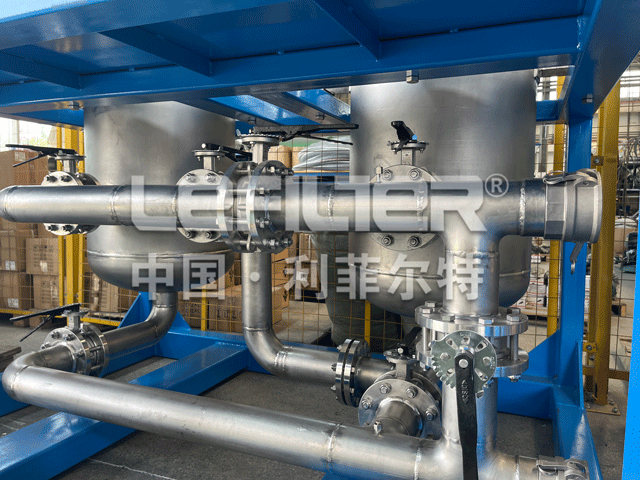
What are the advantages of duplex filters?
Product Information
The double filter, also known as the parallel double switching filter, is composed of two single-cylinder filters and a full-bore three-way ball valve. It has a simple structure and is easy to use.
The double filter has good sealing performance, strong circulation capacity, and low probability of side leakage of the filter element. It can accurately ensure the filtration accuracy, and can quickly replace the filter element. It can be cleaned and replaced online without stopping the machine. There is basically no material consumption during the filtration process, which greatly reduces labor costs.
During the working process, when the single-cylinder filter element is clogged to a certain extent and needs to be cleaned or replaced, the host must be stopped to replace the filter element. This not only wastes time but also fails to meet the needs of the host for continuous operation. Our company independently developed the double filter Effectively solves the shortcomings of single-cylinder filters in this regard.
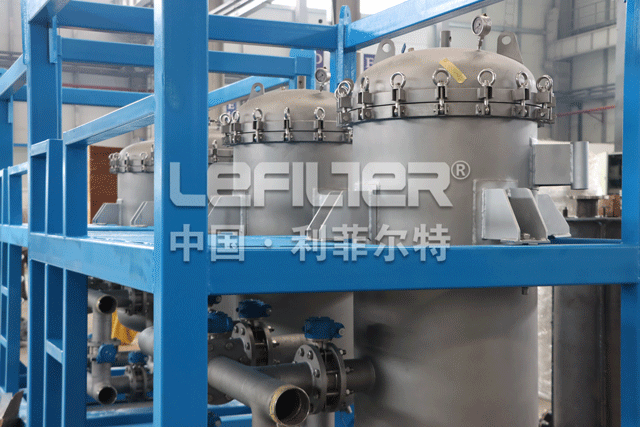
Structural Principles
The double filter cartridge is equipped with a stainless steel filter screen and a filter support basket, and a release valve is installed on the top to discharge the air in the filter; the upper cover and the filter cartridge are connected with a quick-open structure, making it easier to clean and replace the filter. Net, the inlet and outlet valves adopt three-way ball valves to open and close, which are pressure-resistant and temperature-resistant.
Application Areas
Double filters are widely used in hydraulic systems and industrial quenching oil cooling systems. They can work continuously without stopping. They can also be used for RO security filtration, seawater desalination pretreatment, etc.
Petrochemical:
In petrochemical production, it can filter weakly corrosive materials (such as water, ammonia, oil, hydrocarbons, etc.)
Fine Chemicals:
Corrosive materials in chemical production (such as caustic soda, concentrated and dilute sulfuric acid, carbonic acid, acetic acid, etc.)
Refrigeration industry:
Low-temperature materials in refrigeration (such as liquid methane, liquid ammonia, liquid oxygen and various refrigerants)
Light industry and pharmaceutical industry:
It can filter light industrial food and materials with hygienic requirements in pharmaceutical production (such as beer, beverages, dairy products, grain pulp and medical supplies, etc.)